3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(11):3199-3208. doi:10.7150/jca.71925 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of circadian clock genes as regulators of immune infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410006, P.R. China.
2. Department of Internal Medicine, College of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan 410208, P.R. China.
3. School of Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, P.R. China.
Abstract
Background: Multiple studies have reported that the immune system is under the control of a circadian clock, especially in cancers, but how circadian clock genes shape tumor immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear.
Methods: The rhythmicity of circadian clock genes was investigated using the GETx database. The expression and methylation level of circadian clock genes in HCC and paracancerous was evaluated using the GETx and TCGA databases. The differential expression of circadian clock genes in HCC was analyzed using the “limma” package of the R 4.0.4 software. The prognosis of each circadian clock gene was accessed by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. Quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) was carried out to confirm the results. The relationship between circadian rhythm and immune infiltration in HCC was evaluated using the TIMER database and the CIBERSORT algorithm.
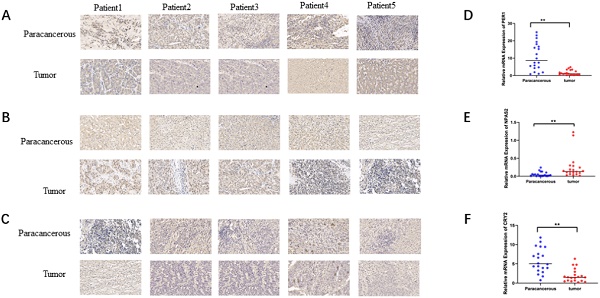
Results: In addition to RORA, RORB, and ARNTL2, there was a rhythmic expression of other circadian clock genes in liver tissue. The correlation between the expression of circadian clock genes differed when comparing HCC and liver tissue. HCC patients who express low levels of PER-1and CRY2 had a poor overall survival (OS). In contrast, patients with higher expression of NPAS2 had a poor prognosis. In HCC, the expression of the PER-1, CRY2, and NPAS2 genes was closely related to immune infiltration.
Conclusion: Our study indicated the disruption of the expression of circadian clock-regulated genes in HCC and identified PER-1, CRY2, and NPAS2 as independent predictors of survival. These genes may be applied as candidate molecular targets for diagnosis and therapy of HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Circadian clock, Immune infiltration, Chrono-immunotherapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact