3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(1):129-139. doi:10.7150/jca.78138 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Optimizing Genomic Control in Hit Network-Target Set Model Associations with Lung Adenocarcinoma
1. Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Dongzhimen, Beijing 100700, China.
2. Postdoctoral Research Station, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China.
3. The Open University of China 75 Fuxing Rd, Haidian District, Beijing 100039.
4. The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (ZhejiangXinhuaHospital), Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, China.
5. Rongcheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Weihai 264399, China.
6. Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Dongzhimen, Beijing 100700, China.
7. Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Haiyuncang, Beijing 100700, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
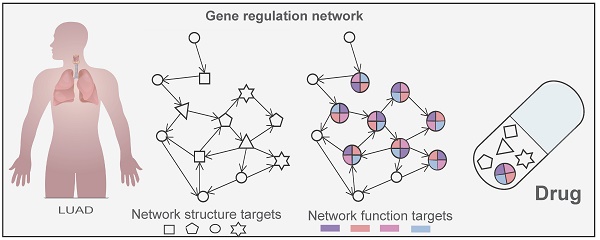
Background: Hit network-target sets (HNSs), compiled sets of different network nodes of the same type, are available and play a significant role in cancer development but are notoriously more difficult to select than a single target. This is due to a combination of challenges attributed to the differential of node interactions, node heterogeneity, and the limitations of node-hit information.
Methods: In this study, we constructed a lung adenocarcinoma regulatory network using TCGA data and obtained different HNSs of driver nodes (DNs), core modules (CMs) and core nodes (CNs) through three kinds of methods. Then, the optimized HNS (OHNS) was obtained by integrating CMs, CNs and DNs, and the performance of different HNSs was evaluated according to network structure importance, control capability, and clinical value.
Results: We found that the OHNS has two main advantages, the central location of the network and the ability to control the network, and it plays an important role in the disease network through its multifaceted capabilities. Three unique pathways were discovered in the OHNS, which is consistent with previous experiments. Additionally, 13 genes were predicted to play roles in risk prognosis, disease drivers, and cell perturbation effects of lung adenocarcinoma, of which 12 may be candidates for new drugs and biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma.
Conclusion: This study can help us understand and control a network more effectively to determine the development trend of a disease, design effective multitarget drugs, and guide the therapeutic community to optimize appropriate strategies according to different research aims in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Network control, Hit network-target sets, Driver nodes, Core module, Core nodes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact