3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(8):1293-1300. doi:10.7150/jca.83747 This issue Cite
Research Paper
WDR4 gene polymorphisms and Wilms tumor susceptibility in Chinese children: A five-center case-control study
1. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Guangzhou Institute of Pediatrics, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Research in Structural Birth Defect Disease, Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Guangzhou 510623, Guangdong, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Biobank, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang, China.
3. Department of Pediatric Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710004, Shaanxi, China.
4. Department of Pediatric Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan, China.
5. Department of Hematology, The Key Laboratory of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Diseases of Wenzhou, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang, China.
6. Department of Pathology, Children Hospital and Women Health Center of Shanxi, Taiyuan 030013, Shannxi, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
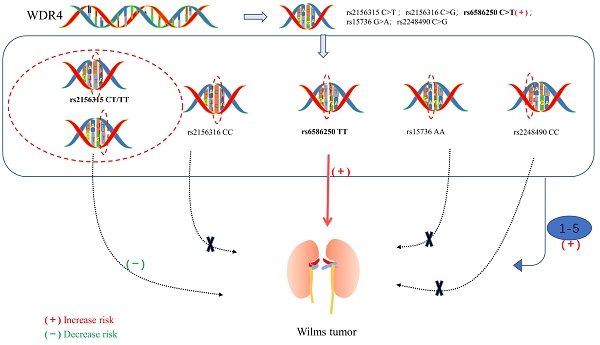
Wilms tumor is the most common embryonal renal malignancy in children. WDR4 is an indispensable noncatalytic subunit of the RNA N7-methylguanosine (m7G) methyltransferase complex and plays an essential role in tumorigenesis. However, the relationship between polymorphisms in the WDR4 gene and susceptibility to Wilms tumor remains to be fully investigated. We performed a large case-control study involving 414 patients and 1199 cancer-free controls to investigate whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the WDR4 gene are associated with Wilms tumor susceptibility. WDR4 gene polymorphisms (rs2156315 C > T, rs2156316 C > G, rs6586250 C > T, rs15736 G > A, and rs2248490 C > G) were genotyped using the TaqMan assay. In addition, unconditioned logistic regression analysis was performed, odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to assess the association between WDR4 gene SNPs and Wilms tumor susceptibility as well as the strength of the associations. We found that only the rs6586250 C>T polymorphism was significantly associated with an increased risk of Wilms tumor (adjusted OR=2.99, 95% CI = 1.28-6.97, P = 0.011 for the rs6586250 TT genotype; adjusted OR=3.08, 95% CI = 1.33-7.17, P = 0.009 for the rs6586250 CC/CT genotype). Furthermore, the stratification analysis revealed that patients with the rs6586250 TT genotype and carriers with 1-5 risk genotypes exhibited statistically significant associations with increased Wilms tumor risk in specific subgroups. However, the rs2156315 CT/TT genotype was identified as having a protective effect against Wilms tumor in the age >18 months subgroup compared with the rs2156315 CC genotype. In brief, our study demonstrated that the rs6586250 C > T polymorphism of the WDR4 gene was significantly associated with Wilms tumor. This finding may contribute to the understanding of the genetic mechanism of Wilms tumor.
Keywords: Wilms tumor, susceptibility, WDR4, polymorphism, m7G modification

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact