3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(12):2236-2245. doi:10.7150/jca.84363 This issue Cite
Research Paper
QiLing Decoction promotes ferroptosis of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells by inhibiting FSP1 in vitro and in vivo
Surgical Department I (Urology Department), LONGHUA Hospital Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 725 Wanping Road South, Xuhui District, Shanghai 200032, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
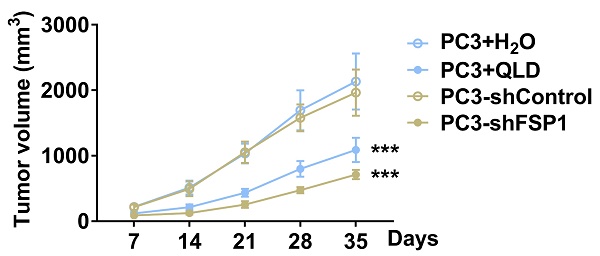
QiLing Decoction (QLD) showed therapeutic effects against prostate cancer with an unclear underlying mechanism. This study explored the underlying mechanisms of QLD against castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Clinical specimens were collected from the patients with CRPC. Stable cells including knockdown and overexpression cell lines were established by plasmid transfection. The xenograft animal model was constructed. Cell viability was determined by using cell-counting kit 8 assay. Biochemical assays were used to determine the levels of iron (Fe2+) and lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS). qRT-PCR and Western blotting were used to determine levels of target genes, respectively. Treatment of QLD inhibited ferroptosis suppressor protein (FSP) 1 at mRNA and protein levels in patients with CRPC. Additionally, cells treated with QLD-containing serum displayed a decrease in cell viability and an increase in Fe2+ and lipid ROS with or without erastin, whereas ferroptosis inhibitor reversed QLD-induced ferroptosis. The regulatory effects of QLD on PC3 cell ferroptosis were associated with its inhibitory effects against FSP1. Consistently, QLD inhibited PC3 tumor growth by inhibiting FSP1. Moreover, treatment of QLD increased the sensitivity of PC3-AbiR cells to abiraterone by inhibiting FSP1. QLD promoted ferroptosis in CRPC cells in part by inhibiting FSP1 in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: Qiling Decoction, prostate cancer, castration-resistant prostate cancer, ferroptosis, FSP1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact