3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(14):2655-2669. doi:10.7150/jca.87184 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of Tumor Antigens and Immune Subtypes of High-grade Serous Ovarian Cancer for mRNA Vaccine Development
1. Department of Radiation Oncology, Cancer Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong, China.
2. Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong, China.
*These 2 authors contributed equally to this project.
Abstract
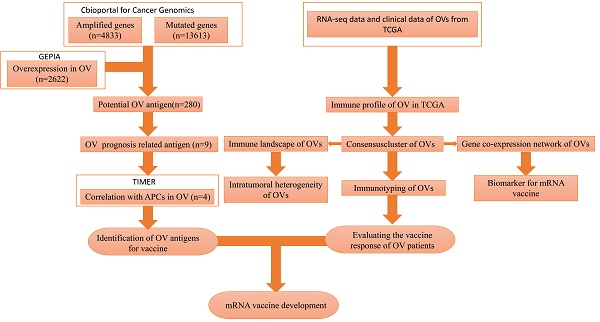
High-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSC) is the most common pathology of ovarian cancer and has aggressive characteristics and poor prognosis. mRNA vaccines are a novel tool for cancer immune treatment and may play an important role in HGSC therapy. Our study aimed to explore tumour antigens for vaccine development and identify potential populations amenable to vaccine treatment. Based on transcription data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we identified four tumour-specific antigens for vaccine production: ARPC1B, ELF3, VSTM2L, and IL27RA. In addition to being associated with HGSC patient prognosis, the expression of these antigens was positively correlated with the abundances of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Furthermore, we stratified HGSC samples into three immune subtypes (IS1-IS3) with different immune characteristics. A corhort from ICGC (International Cancer Genome Consortium) was used to validate. Patients of IS3 had the best prognosis, while patients of IS1 were most likely to benefit from vaccination. There was substantial heterogeneity in immune signatures and immune-associated molecule expression in HGSC. Finally, weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) was employed to cluster immune-related genes and explore potential biomarkers related to vaccination. In conclusion, we identified four potential tumour antigens for mRNA vaccine production for HGSC treatment, and the immune subtype could be an important indicator to select suitable HGSC patients to receive vaccination.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact