3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(17):3351-3367. doi:10.7150/jca.88650 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Pan-cancer Analysis of the Disulfidptosis-related Gene NCKAP1 and Its Prognostic Value for Lung Adenocarcinoma
1. The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China.
2. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China.
# Co-first authors
Abstract
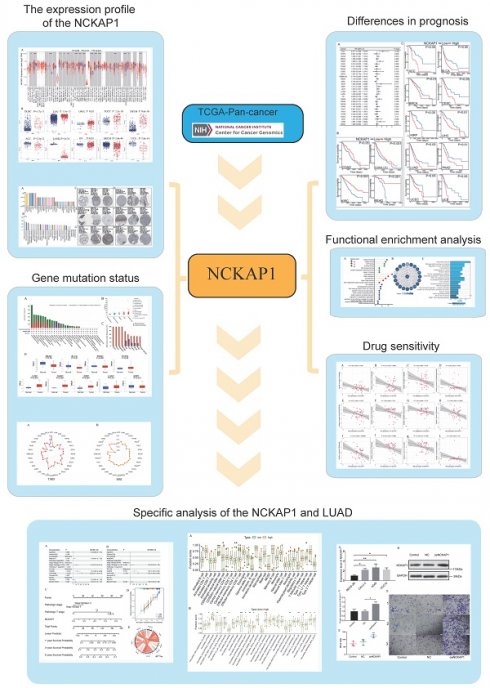
Background: The nck-associated protein 1 (NCKAP1) of the disulfidptosis-related gene is essential in programmed cell death. However, a comprehensive analysis of the biological significance of NCKAP1 in pan-cancer is lacking.
Methods: Gene expression matrices and clinical expression information of cancers were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype Tissue Expression (GTEX) databases. A comprehensive analysis of NCKAP1 expression, biological function, gene mutation, immune cell infiltration, DNA methylation, and drug sensitivity profiles in pan-cancer was performed using the Timer2.0, HPA, GEPIA, STRING, cBioPortal, UALCAN and CellMiner databases. The prognostic value of NCKAP1 was investigated based on COX regression analysis and the Kaplan-Meier(K-M) curves. A nomogram was established to verify the clinical value of NCKAP1 for LUAD. The correlation between NCKAP1 and immune cells and signaling pathways were investigated by single-sample gene set enrichment analysis(ssGSEA). Validation was performed using PCR, Western Blot (WB), and Transwell assays.
Result: Significant differences in expression levels, mutation levels, and methylation levels of NCKAP1 between tumor and normal samples. NCKAP1 affects the prognosis of various cancers. NCKAP1 is strongly associated with microsatellite instability (MSI) and tumor mutational burden (TMB). The Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses indicate that NCKAP1 is strongly associated with cell death and tumor immunity. The expression of NCKAP1 affects the sensitivity to various drugs. Moreover, NCKAP1 is an independent predictor of prognosis in LUAD patients. The results of ssGSEA showed that elevated NCKAP1 expression was positively correlated with multiple immune-related signaling pathways. PCR analysis showed that the expression of NCKAP1 was increased in LUAD cells. Transwell invasion assay showed that overexpression of NCKAP1 resulted in enhanced invasion of LUAD cells.
Conclusions: We comprehensively analyzed the relationship between NCKAP1 and pan-cancer and its potential clinical value. NCKAP1 could be a potential immune marker for various cancers (especially LUAD), providing new insights and insights for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Pan-cancer, immune, Lung adenocarcinoma, prognosis, biomarkers, Transwell.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact