3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(6):1642-1656. doi:10.7150/jca.89219 This issue Cite
Review
The Emerging Function and Promise of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Cancer
1. College of Resources, Environment and Chemistry, Chuxiong Normal University, Chuxiong 675000, China.
2. College of Basic Medical Sciences, Dali University, Dali 671000, China.
3. College of Foreign Languages, Chuxiong Normal University, Chuxiong 675000, China.
4. The People's Hospital of ChuXiong Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Chuxiong 675000, China.
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
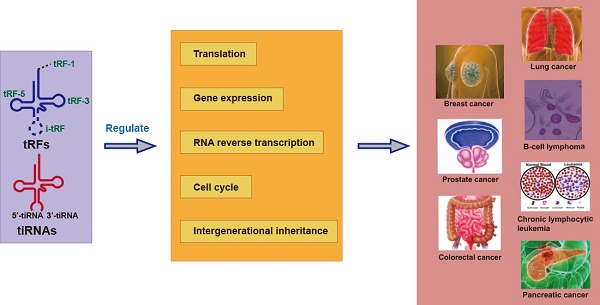
Fragments derived from tRNA, called tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs), have attracted widespread attention in the past decade. tsRNAs are widespread in prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcriptome, which contains two main types, tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) and tRNA-derived stress-inducing RNA (tiRNAs), derived from the precursor tRNAs or mature tRNAs. According to differences in the cleavage position, tRFs can be divided into tRF-1, tRF-2, tRF-3, tRF-5, and i-tRF, whereas tiRNAs can be divided into 5'-tiRNA and 3'-tiRNA. Studies have found that tRFs and tiRNAs are abnormally expressed in a variety of human malignant tumors, promote or inhibit the proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells by regulating the expression of oncogene, and play an important role in the aggressive metastasis and progression of tumors. This article reviews the biological origins of various tsRNAs, introduces their functions and new concepts of related mechanisms, and focuses on the molecular mechanisms of tsRNAs in cancer, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, b-cell lymphoma, and chronic lymphoma cell leukemia. Lastly, this article puts forward some unresolved problems and future research prospects.
Keywords: tsRNAs, tRF, tiRNA, cancer, molecular mechanisms

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact