3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(9):2691-2711. doi:10.7150/jca.93975 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Discovery of a novel ROS-based signature for predicting prognosis and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma
1. National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 100021.
2. CAMS Key Laboratory of Translational Research on Lung Cancer, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 100021.
3. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing, China, 100044.
Abstract
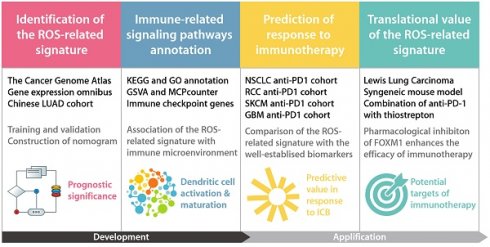
The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is critical in the emergence and progression of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), affecting cell survival, proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Further investigations are needed to elucidate these effects' precise pathways and devise therapeutic approaches targeting ROS. Moreover, the expression pattern and clinical significance of the ROS-related genes in LUAD remain elusive. Through comprehensive analysis incorporating 1494 LUAD cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas, six Gene Expression Omnibus series, and a Chinese LUAD cohort, we identified a ROS-related signature with substantial predictive value in various LUAD patient cohorts. The ROS-related signature has demonstrated a significant negative relationship with antitumor immunity and dendritic cell maturation and activation. Moreover, The ROS-related signature showed predictive value on immunotherapy outcomes across multiple types of solid tumors, including LUAD. These findings reinforce the ROS-related signature as a predictive tool for LUAD and provide new insights into its link with antitumor immunity and immunotherapy efficacy. These results have implications for refining clinical assessments and tailoring immunotherapeutic strategies for patients with LUAD.
Keywords: dendritic cells, immunotherapy, LUAD, ROS, tumor microenvironment.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact