Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2021; 12(15):4497-4504. doi:10.7150/jca.58094 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinical significance of C-Reactive Protein to Lymphocyte Count Ratio as a prognostic factor for Survival in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients undergoing Curative Surgical Resection
1. Department of Allergy, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Medical Oncology & Hematology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4. College of Nursing, Hallym Polytechnic University, Gangwon-do, Republic of Korea.
5. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
6. Department of Clinical Oncology, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
*Co-first authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
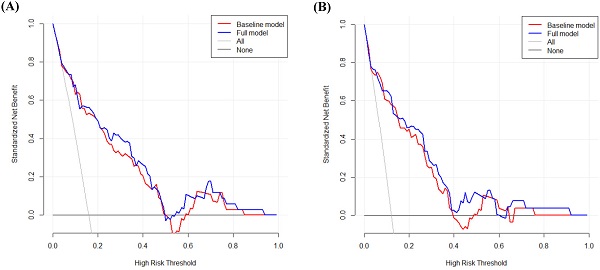
Purpose: We assessed the clinical feasibility of C-reactive protein to lymphocyte ratio (CLR) as a determinant of survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) undergoing curative surgical resection.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on patients with stage I and II NSCLC undergoing curative resection. Demographic and clinical variables, including CLR, were collected and analyzed. The Cox proportional hazards model was used to calculate hazard ratios for overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare differences between two independent groups.
Results: The median age of the patients was 69.0 years, and male patients comprised 63.9% of all patients. A total of 164 (75.9%) patients were categorized as having stage I disease and 52 (24.1%) as having stage II disease. Using the multivariate Cox model, age (hazard ratio [HR] 1.08, p<0.001), lymphatic invasion (HR 3.12, p=0.004), stage (HR 5.10, p<0.001), and CLR (HR 1.01, p=0.003) were significant determinants of OS. In addition, age (HR 1.11, p=0.002), lymphatic invasion (HR 3.16, p=0.010), stage (HR 6.89, p<0.001), and CLR (HR 1.05, p=0.002) were significant determinants of CSS.
Conclusions: Our findings show that CLR could be a determinant of survival in NSCLC patients undergoing curative surgical resection.
Keywords: Carcinoma, Non-Small Cell Lung, Pulmonary Surgical Procedures, Prognosis, Lymphocyte Count, C-Reactive Protein

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact