3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2022; 13(15):3701-3709. doi:10.7150/jca.78498 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Exonuclease 1 genetic variant is associated with clinical outcomes of pemetrexed chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma
1. Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
2. Cell and Matrix Research Institute, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
3. Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
4. BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Department of Biomedical Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
5. Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
6. Department of Radiology School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
7. Medical Research Collaboration Center in Kyungpook National University Hospital and School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
8. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Gumi, Korea.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
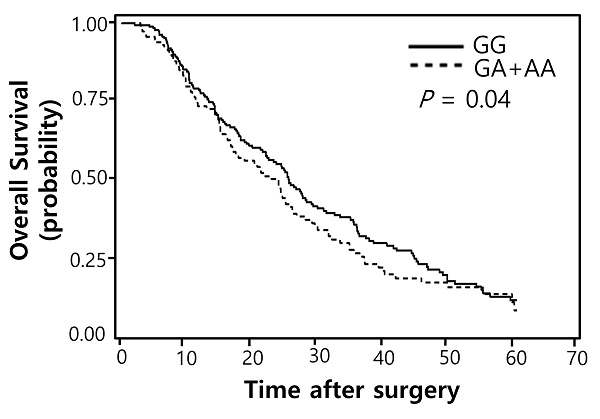
Pemetrexed is an anti-folate agent which is one of the most frequently used chemotherapy agents for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. However, clinical response to pemetrexed chemotherapy and survival outcome of patients varies significantly. We evaluated whether the genetic variants in miRNA target sites may affect the treatment outcome of pemetrexed chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma patients. One hundred SNPs in miRNA binding regions in cancer-related genes were obtained from the crosslinking, ligation, and sequencing of hybrids (CLASH) and CancerGenes database, and the associations with the response to pemetrexed chemotherapy and survival outcomes were investigated in 314 lung adenocarcinoma patients. Two polymorphisms, EXO1 rs1047840G>A and CAMKK2 rs1653586G>T, were significantly associated with worse chemotherapy response (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.41, 95% CI = 0.24-0.68, P = 0.001, under dominant model; and aOR = 0.33, 95% CI = 0.16-0.67, P = 0.002, under dominant model, respectively) and worse OS (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 1.34, 95% CI = 1.01-1.77, P = 0.04, under dominant model; and aHR = 1.50, 95% CI = 1.06-2.13, P = 0.02, under dominant model, respectively) in multivariate analyses. Significantly increased luciferase activity was noted in EXO1 rs1047840 A allele compared to G allele. In conclusion, two SNPs in miRNA binding sites, especially EXO1 rs1047840G>A, were associated with the chemotherapy response and survival outcome in lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with pemetrexed.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, miRNA target sites, genetic variants, chemotherapy, response, survival

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact