3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2023; 14(12):2289-2300. doi:10.7150/jca.85906 This issue Cite
Research Paper
FOXP1-GINS1 axis promotes DLBCL proliferation and directs doxorubicin resistance
1. Key Laboratory of Developmental Genes and Human Disease in Ministry of Education, Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Critical Care Medicine, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medical School of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, China.
3. Department of Hematology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, China.
4. Department of ultrasound, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, China.
Abstract
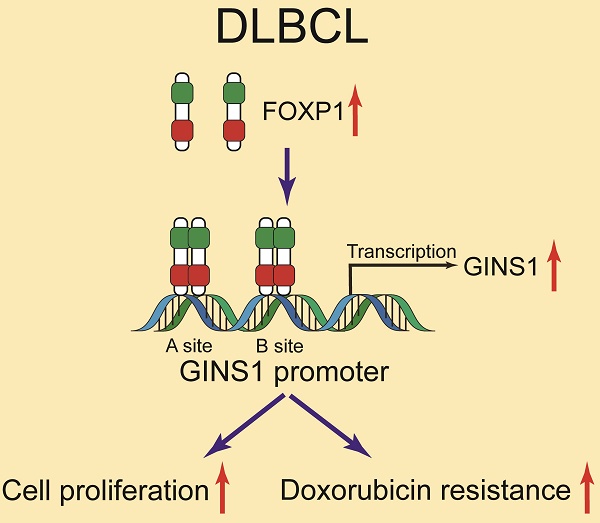
GINS1 is overexpressed in several types of cancers including leukemia and linked to poor outcomes. However, GINS1 remains poorly investigated in DLBCL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). This project aimed to explore the expression, functions and regulation of GINS1 in DLBCL. In this study, through analysis of clinical specimens from DLBCL patients, we uncovered that GINS1 was upregulated in DLBCL. By EMSA, ChIP and luciferase reporter assays, it was found that FOXP1 transcriptionally activated GINS1 expression by directly binding to the promoter region of the GINS1 gene. Western blotting and RT-PCR also revealed that GINS1 expression positively correlated with FOXP1 in human DLBCL specimens and cell lines. In an in vivo xenograft lymphoma mouse model, the FOXP1/GINS1 regulatory axis was also validated. Moreover, with CCK8 cell proliferation assays and colony formation assay, elevated GINS1 expression was found to be associated with doxorubicin resistance in lymphoma cells. Our findings showed that the FOXP1-GINS1 axis played a critical role in DLBCL development and doxorubicin resistance, and targeting the FOXP1-GINS1 axis could be a potential therapeutic approach for DLBCL treatment.
Keywords: FOXP1, GINS1, DLBCL, transcription, B cell

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact