3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1837-9664
J Cancer 2024; 15(1):166-175. doi:10.7150/jca.87758 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Expression and role of FKBPL in lung adenocarcinoma
1. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Tumour Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Nantong Sixth People's Hospital, Nantong, China.
† Lili She and Xingsong Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
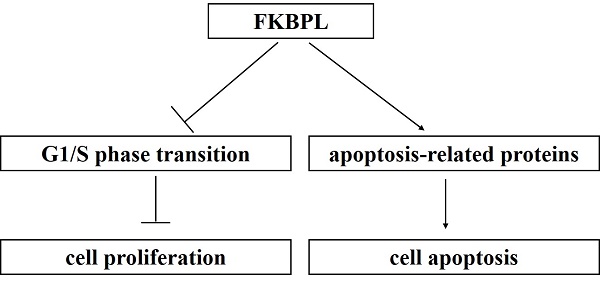
Dysregulated expression of FK506-binding protein like (FKBPL) has been demonstrated to play crucial roles in tumour development. However, the role of FKBPL in lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) remains unclear. Using immunohistochemical staining, we showed that FKBPL expression was significantly lower in lung ADC than the normal tissues (P < 0.0001). Patients with well or moderately differentiated tumours have higher FKBPL expression compared with patients with poor differentiated tumours (P = 0.037). However, no significant associations were found between FKBPL expression and other clinicopathological variables (P > 0.05 for all). Cox univariate analysis showed that high FKBPL expression was correlated with prolonged overall survival (OS) (P = 0.010). Kaplan-Meier analysis further confirmed that the FKBPL-low group showed a significantly shorter OS than the FKBPL-high group (P = 0.0081). FKBPL expression was not shown as an independent prognostic factor for OS in the multivariate analysis (P = 0.063). Moreover, our study demonstrated that FKBPL could suppress the proliferation of lung ADC cells by delaying cell cycle G1/S phase transition. In addition, FKBPL resulted in increased apoptosis in lung ADC cells. Using the Human Apoptosis Array Kit, we observed that overexpression of FKBPL in lung ADC A549 cells significantly decreased the anti-apoptotic proteins, including heat shock protein 32 (HSP32), heat shock protein 27 (HSP27), and paraoxonase-2 (PON2). FKBPL depletion significantly attenuated the pro-apoptotic protein, phospho-p53 (S46), in lung ADC H1975 cells. These new findings provide an experimental basis for further theoretical investigation of lung ADC.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, FKBPL, overall survival, cell proliferation, cell apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact